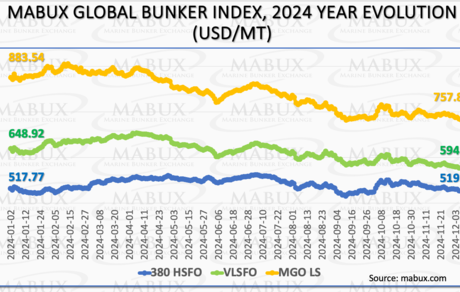
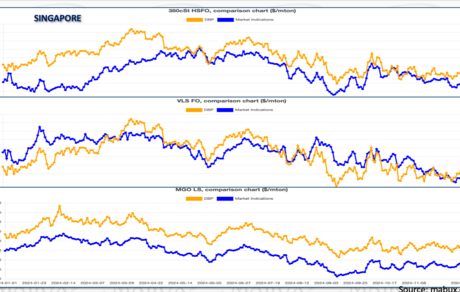
The global bunker market ended 2024 in a state of relative stability. In the first half of the year, multidirectional fluctuations were observed across indices, with moderate increases in 380 HSFO and VLSFO prices and a slight decline in MGO LS quotes. In the second half, the amplitude of these fluctuations significantly decreased. From September onward, trends for all three types of bunker fuel stabilized at their respective levels. By year-end, the 380 HSFO Index remained virtually unchanged, rising by just USD 1.96, while the VLSFO Index and MGO LS Index declined by USD 54.00 and USD 125.66, respectively. Looking ahead to early 2025, we expect global bunker indices to lack a pronounced trend and continue exhibiting multidirectional movements.
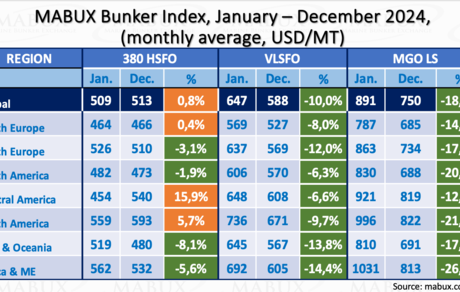
Regionally, the 380 HSFO segment experienced mixed dynamics in 2024. Central and South America recorded price increases of 15.9% and 5.7%, respectively, while all other regions saw moderate declines ranging from 2% to 8%. In the VLSFO segment, prices fell across all regions, with declines ranging from 6% to 14%. A similar trend occurred in the MGO LS segment, where prices dropped by 17% to 26%. The sharpest declines in 380 HSFO were seen in Asia/Oceania (-8.1%), while VLSFO and MGO LS recorded their steepest drops in Africa/Middle East at -14.4% and -26.8%, respectively.
Scrubber Spread (SS)
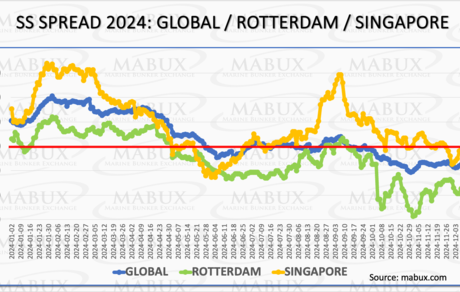
In 2024, the MABUX Global Scrubber Spread (Global SS)—the price difference between 380 HSFO and VLSFO—remained confidently above the $100.00 mark during the first half of the year, maintaining the profitability of the 380 HSFO + Scrubber combination (SS Breakeven). However, by June, the indicator approached SS Breakeven, showing fluctuating trends around this level until October. In the final quarter, Global SS fell below $100.00, consolidating in the range of $73.00–$76.00 by year-end. This continued reduction in the SS Spread reflects declining economic efficiency and profitability for the 380 HSFO + Scrubber combination in the global bunker market.
In Rotterdam and Singapore, SS Spread dynamics mirrored the global trend:
• Rotterdam: The SS Spread fell below $100.00 from May onward and hit a record low of $14.00 at the end of October. However, it corrected upwards by year-end, stabilizing at approximately $60.00.
• Singapore: The SS Spread displayed greater stability, staying at or above the $100.00 mark until November. In December, it fell below SS Breakeven, fluctuating between $85.00–$95.00.
Despite the SS Spread falling consistently below the $100.00 threshold, the adoption of scrubbers continued to grow. According to DNV, the total number of ships with scrubbers installed or in operation reached 5,790 in 2024, up from 4,875 in 2022 and 5,375 in 2023. The primary customers for scrubbers remain the large-tonnage fleet, including bulk carriers, container ships, and tankers.
MABUX Market Differential Index (MDI)
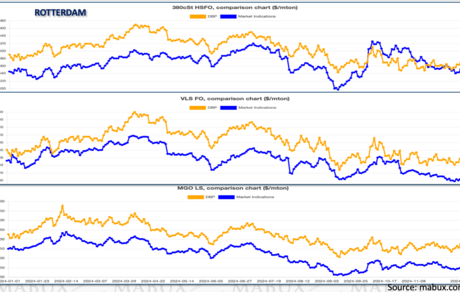
In 2024, the MABUX Market Differential Index (MDI), which compares market bunker prices (MBP) with the MABUX digital bunker price benchmark (DBP), revealed a prevailing trend of underpricing for all fuel types in Rotterdam and Singapore.
Rotterdam:
• 380 HSFO: The MDI showed average undervaluation of USD 53/MT in Q1, USD 51/MT in Q2, and USD 36/MT in Q3. A brief overvaluation surge occurred in October-November (+15–45 USD/MT), but the year closed with undervaluation.
• VLSFO: Fuel remained undervalued throughout the year, with averages of -30 USD/MT, -61 USD/MT, -50 USD/MT, and -38 USD/MT across the four quarters.
• MGO LS: Underpricing levels were more pronounced, averaging -98 USD/MT, -91 USD/MT, -112 USD/MT, and -100 USD/MT.
Singapore: Despite the prevailing underpricing in the 380 HSFO and MGO LS segments, the difference in market prices compared to the MABUX digital benchmark was not as significant as in Rotterdam.
• 380 HSFO: Underpricing averaged -63 USD/MT in Q1, -31 USD/MT in Q2, -31 USD/MT in Q3, and -13 USD/MT in Q4.
• VLSFO: The MDI revealed moderate overvaluation in Q1 (+27 USD/MT), Q3 (+10 USD/MT), and Q4 (+11 USD/MT), while Q2 saw undervaluation of -20 USD/MT.
• MGO LS: Undervaluation remained consistent, with values of -95 USD/MT (Q1), -101 USD/MT (Q2), -112 USD/MT (Q3), and -98 USD/MT (Q4).
The global bunker market dynamics suggest that the trend of undervaluation across all bunker fuel types will likely persist in the short term.
LNG as a bunker fuel
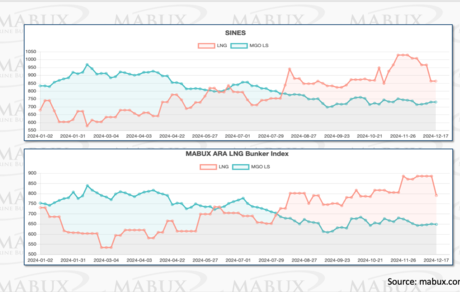
Since the beginning of August 2024, global gas indices, in particular TTF, have shown a steady upward trend. TTF has been consistently above 35 EUR/MWh, and even briefly exceeded 48 EUR/MWh in early December. This trend has directly influenced the growth of LNG prices as a bunker fuel. If in the first half of 2024 LNG prices were lower than the cost of the most expensive type of traditional bunker fuel MGO LS in the port of Sines (Portugal) by an average of 247 USD/MT in the first quarter and 114 USD/MT in the second quarter, and in ARA by 164 USD/MT and 108 USD/MT, respectively, then by August last year the cost ratio changed in favor of MGO LS and amounted to plus 47 USD/MT and plus 191 USD/MT in the third and fourth quarters in the port of Sines and plus 46 USD/MT and plus 168 USD/MT in ARA.
Currently, the price difference fluctuates between 200 and 250 USD/MT in the port of Sines and between 140 and 230 USD/MT in ARA in favor of MGO LS. However, despite this price difference, LNG remains the most popular choice for the shipping industry to switch to alternative bunker fuels at the moment. This is primarily due to strong demand in the container ship segment, supported by a well-developed LNG bunkering infrastructure and a steady growth in the number of LNG-powered vessels. According to DNV, the number of LNG-powered vessels (on order and already in service) reached 723 units in 2024, compared to 354 in 2022 and 472 in 2023, which underlines the growing popularity of LNG in the maritime sector.
In the medium term, a significant reduction in the price gap between LNG and MGO appears unlikely. However, this is not expected to deter the expansion of the LNG fleet segment. LNG continues to be viewed as the most cost-effective, accessible, and viable alternative fuel for the shipping industry.
Overall, the situation in the global bunker market remains fairly stable given the current balance of fundamental factors of supply and demand. However, any escalation in geopolitical tensions could cause a temporary spike in bunker prices. Additionally, a change in the segmentation of the regional bunker market in the Mediterranean towards more environmentally friendly fuels is expected due to the declaration of this region as an Emission Control Area (MedECA) from May 1, 2025. Despite this, significant structural changes in the global bunker market in 2025 are unlikely.
By Sergey Ivanov, Director, MABUX