The Bunker Outlook was contributed by Marine Bunker Exchange (MABUX)
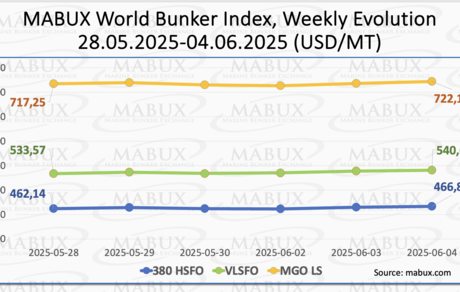
At the close of Week 23, the global bunker indices published by MABUX showed moderate gains. The 380 HSFO index increased by $4.69, rising from $462.14/MT to $466.83/MT. The VLSFO index climbed by $7.03, reaching $540.60/MT compared to $533.57/MT the previous week. Meanwhile, the MGO index rose by $4.92, from $717.25/MT to $722.17/MT. As of the time of writing, the market continued to exhibit a moderate upward trend.
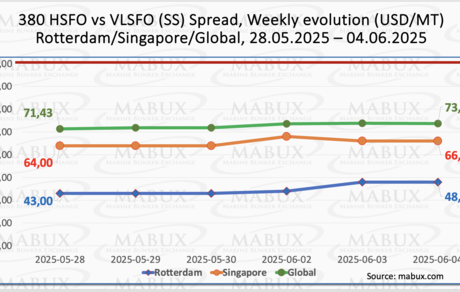
The MABUX Global Scrubber Spread (SS) – the price difference between 380 HSFO and VLSFO – increased by $2.34, rising from $71.43 last week to $73.77. The average weekly value of the index also saw a modest increase of $0.64. In Rotterdam, the SS Spread rose by $5.00, from $43.00 to $48.00, with the port’s average weekly value up by $1.16. In Singapore, the 380 HSFO/VLSFO price differential widened by $2.00, reaching $66.00 from $64.00 last week. However, the average weekly value in the port declined by $2.34. Overall, no consistent trend has emerged in the dynamics of the global or port-specific SS Spread indices, which continue to show fluctuations. With the index still well below the $100.00 breakeven threshold, conditions remain favorable for the continued use of conventional VLSFO over 380 HSFO paired with scrubbers. We do not anticipate any significant changes in SS Spread dynamics in the coming week. More detailed information is available in the Differentials section of mabux.com.
According to a report by the International Group of Liquefied Natural Gas Importers (GIIGNL), while the long-term outlook for LNG demand remains strong, short- and medium-term projections are increasingly uncertain due to volatile pricing, geopolitical tensions, and uneven economic recovery in key Asian markets. The report notes that while global LNG imports reached 405 million tonnes in 2024 – up from 401 million in 2023 – growth is slowing, and regional dynamics are diverging. Market focus is now on Europe’s storage replenishment pace, LNG demand trends in Asia, and whether North Asia’s demand will increase enough to compete with Europe for spot cargoes.
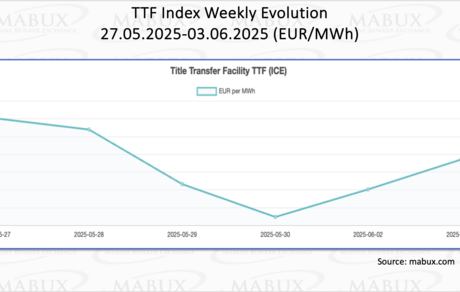
As of June 3, European regional gas storage facilities were 49.20% full – an increase of 2.62 percentage points compared to the previous week, but a decrease of 22.13 points from the beginning of the year (71.33%). A slight acceleration in the pace of storage replenishment has been observed. By the end of Week 23, the European gas benchmark TTF saw a moderate decline, falling by €1.158/MWh to €35.858/MWh from €37.006/MWh the previous week.
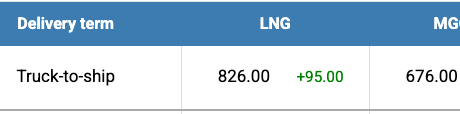
The price of LNG as a bunker fuel at the port of Sines (Portugal) rose by USD 95 over the week, reaching USD 826/MT by the end of the week, up from USD 731/MT the previous week. At the same time, the price gap between LNG and conventional fuel widened significantly. As of June 2, the difference increased to USD 150 in favor of conventional fuel, compared to USD 53 the week before. On the same day, MGO LS was quoted at USD 676/MT at the port of Sines. More detailed information is available in the LNG Bunkering section on mabux.com.
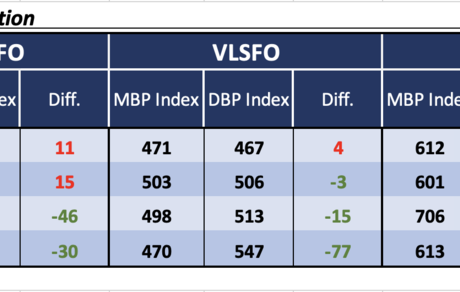
Over the Week 23, the MABUX Market Differential Index (MDI) – which reflects the correlation between market bunker prices (MBP) and the MABUX Digital Bunker Benchmark (DBP) – showed the following trends across the 380 HSFO and VLSFO segments:
• 380 HSFO segment: Rotterdam and Singapore remained in the overvalued zone. The weekly average MDI held steady in Rotterdam but declined by 5 points in Singapore. Fujairah and Houston were undervalued; the MDI rose by 2 points in Fujairah and fell by 2 points in Houston. Notably, Rotterdam's MDI aligns with the 100% correlation point between MBP and DBP.
• VLSFO segment: Singapore shifted into the undervalued zone, joining Fujairah and Houston. The average MDI increased by 6 points in Singapore and by 3 points in Fujairah but declined by 3 points in Houston. Rotterdam remained the only overvalued port in this segment, with a 1-point increase in its average MDI. Both Rotterdam and Singapore are now hovering near the 100% correlation mark between MBP and DBP.
• MGO LS segment: Rotterdam continued to be the only overvalued port, though its weekly average MDI dropped by 5 points. The remaining ports – Singapore, Fujairah, and Houston – were undervalued. The MDI rose by 2 points in Singapore but fell by 2 points in Fujairah and 15 points in Houston.
Overall, there were no major shifts in the overvalued/undervalued balance during the week, except for Singapore's transition to the undervalued zone in the VLSFO segment. The prevailing trend of undervaluation in the global bunker market remains dominant. We do not anticipate significant changes in the valuation balance in the upcoming week.
Further insights into the correlation between market prices and the MABUX digital benchmark are available in the Digital Bunker Prices section of www.mabux.com.
The IMO Net-Zero Policy Review indicates that ammonia-based dual-fuel ships will likely become the most cost-effective option to meet emissions targets by the mid-2030s, though their short-term viability remains uncertain. The study finds that rising greenhouse gas prices will give these ships a clear competitive edge from that point onward. In the near term, a variety of alternative marine fuels could be viable. The authors suggest that LNG will be a competitive option during the early transition phase, but its advantage will diminish rapidly by the early 2030s as stricter emissions targets take effect. The review also notes that the IMO has yet to offer clear guidelines for fuel producers on meeting emissions goals, which is hindering early investment in e-fuels.
We believe the global bunker market retains potential for continued moderate growth next week.
By Sergey Ivanov, Director, MABUX