The Weekly Outlook was contributed by Marine Bunker Exchange (MABUX)
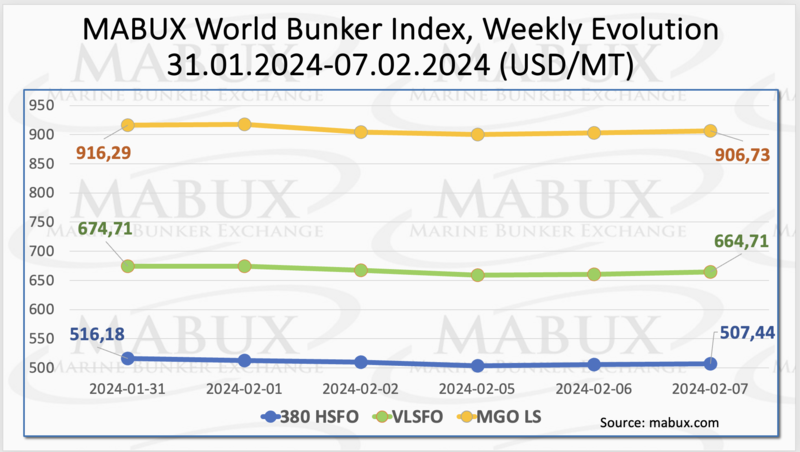
Over the 6th week, the MABUX global bunker indices showed a moderate decline. The 380 HSFO index fell by 8.74 USD: from 516.18 USD/MT last week to 507.44 USD/MT, approaching the 500 USD mark. The VLSFO index, also decreased by 10.00 USD (664.71 USD/MT versus 674.71 USD/MT last week). The MGO index lost 9.56 USD (from 916.29 USD/MT last week to 906.73 USD/MT). At the time of writing, the market has shown a moderate upward correction.
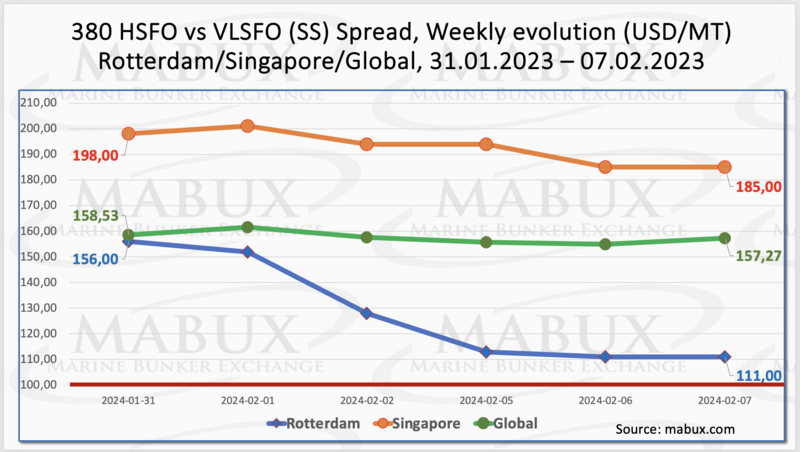
Global Scrubber Spread (SS) - the price difference between 380 HSFO and VLSFO - experienced a slight decrease: minus $1.26 ($157.27 versus $158.53 last week. The weekly average, on the contrary, increased by $3.28. In Rotterdam, SS Spread significantly dropped by $45.00 (from $156.00 last week to 111.00), nearing the $100 mark (SS breakeven), while the weekly average increased by a symbolic $0.17. In Singapore, the price difference for 380 HSFO/VLSFO saw a less significant decrease of $13 ($185.00 versus $198.00 last week), breaking through the $200 mark during the week. The weekly average decreased by $1.34. Signs of a shift in the SS Spread trend towards reduction were observed during the week. More information is available in the “Differentials” section of www.mabux.com.
Supplies of liquefied natural gas (LNG) into the EU's gas transportation system from terminals reached a three-month low in January, totaling 10.65 billion cubic meters. This marks a 6% decline compared to December figures and a similar 6% decrease compared to the same period in 2023. Selections from underground gas storage facilities (UGS) in 2024 take the lead among gas production sources in Europe, comprising 41%. LNG holds the second position with a 23% share, while supplies from the North Sea rank third at 19%. The East, including Russian gas, contributes 7.2%, North Africa provides 6%, and the UK accounts for just 2% of the overall gas supplies.
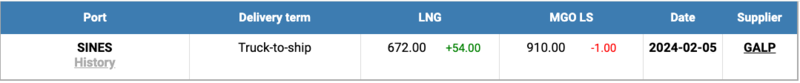
The price of LNG as bunker fuel in the port of Sines (Portugal) showed a moderate increase and reached 672 USD/MT on February 5 (plus 54 USD compared to last week). At the same time, the difference in price between LNG and conventional fuel slightly narrowed on February 05, favoring LNG by 238 USD, compared to the 300 USD difference the previous week. On the same day, MGO LS was quoted at 910 USD/MT in the port of Sines. More information is available in the LNG Bunkering section of www.mabux.com.
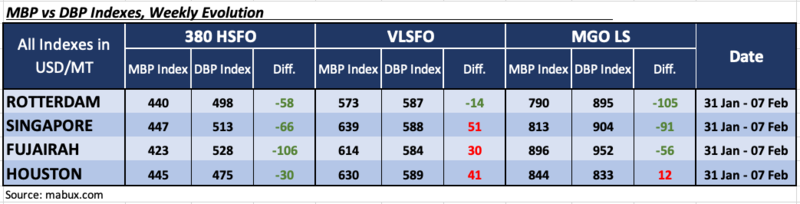
During week 06, the MDI index (the ratio of market bunker prices (MABUX MBP Index) vs. the MABUX digital bunker benchmark (MABUX DBP Index)) recorded the following trends in four selected ports: Rotterdam, Singapore, Fujairah and Houston:
In the 380 HSFO segment, all four selected ports remained in the undervalued zone. The weekly average underpricing fell by 7 points in Rotterdam, 3 points in Singapore, 12 points in Fujairah and 9 points in Houston. The MDI index in Fujairah remains above the $100 mark.
As for the VLSFO segment, according to MDI, three ports: Singapore, Fujairah and Houston were in the overcharge zone. Weekly average overprice premiums rose by 5 points in Singapore, 7 points in Fujairah and 36 points in Houston. Rotterdam remained the only undercharged port, with a weekly average undervaluation level decreasing by 16 points.
In the MGO LS segment, Houston moved into the overvalued zone to be the only overpriced port in this bunker segment. Average weekly premium increased by 29 points. The other three selected ports remained underpriced. Average weekly underprice margins showed an increase in Rotterdam by 9 points, in Singapore by 1 point and in Fujairah by 10 points.
The overall dynamics of the MDI index in major hubs continues to show irregular changes.
More information on the correlation between market prices and the MABUX digital benchmark is available in the “Digital Bunker Prices” section of www.mabux.com.
DNV reported a robust month for alternative fuel orders, revealing that 23 methanol-fueled vessels were ordered in January. The container segment accounted for approximately 70% of these orders, while the remaining vessels were predominantly in the bulk and RoRo segments. Additionally, the database recorded the addition of 10 LNG-fueled ships, with car carriers and tankers dominating these orders, followed by RoPaxes. January saw a remarkable 24 LNG ship deliveries, marking a record for this segment, which has experienced significant growth in recent years, now totaling 493 LNG-fueled ships globally—a remarkable 100% increase compared to 2021. The methanol-fueled ship orderbook is expanding rapidly, currently standing at 228 confirmed orders. This surge in orders is anticipated to substantially augment the existing global fleet of 29 methanol-fueled ships in the coming years. Moreover, interest in ammonia as a fuel is gaining momentum, evidenced by the confirmation of two orders in January.
It is anticipated that the world bunker indices have stabilized at current levels, with no firm trend expected in the market next week.
By Sergey Ivanov, Director, MABUX
All news