The Weekly Outlook was contributed by Marine Bunker Exchange (MABUX)
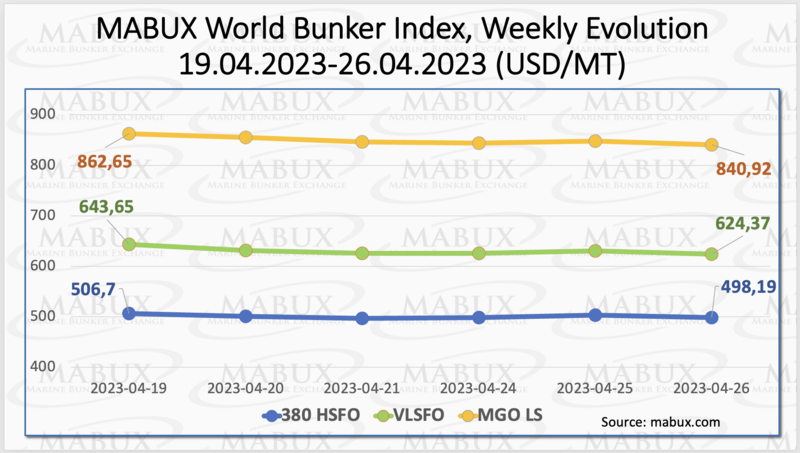
During Week 17, the global MABUX bunker indices showed a consistent downward trend. The 380 HSFO index dropped by 8.51 USD, falling from 506.70 USD/MT last week to 498.19 USD/MT, breaking through the psychological threshold of 500 USD. Similarly, the VLSFO index also declined by 19.28 USD, going from 624.37 USD/MT to 643.55 USD/MT last week. The MGO index also experienced a decrease of 21.73 USD, dropping from 862.65 USD/MT to 840.92 USD/MT. As of the time of writing, the market continued to show downward momentum.
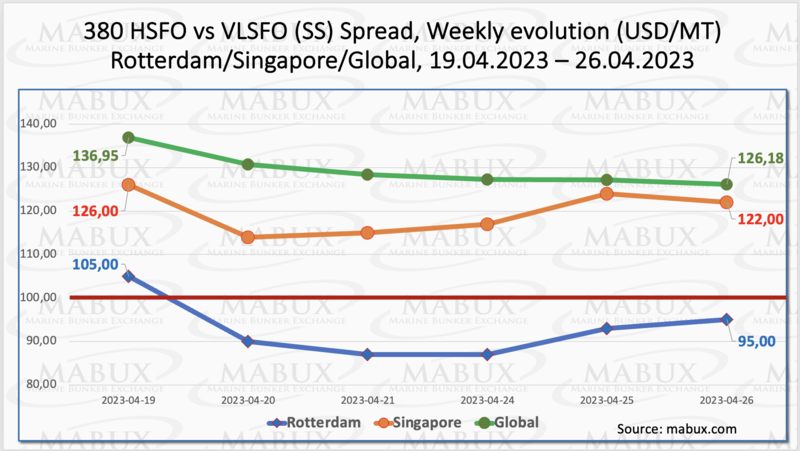
In Week 17, the Global Scrubber Spread (SS), which represents the price difference between 380 HSFO and VLSFO, continued to decline, reaching minus $10.77 ($126.18 vs. $136.95 last week). The weekly average also decreased by $9.82. In Rotterdam, the SS Spread dropped below the $100 mark, hitting $87.00 USD within a week for the first time since October 21, 2021. It is considered that SS Spread below $ 100 makes the use of scrubbers low profitable. The weekly average of SS Spread in Rotterdam also decreased by $14.17. In Singapore, the price difference between 380 HSFO and VLSFO decreased by $4.00 by the end of the week ($122 vs. $126.00 last week), and the average weekly value saw a minimal decrease of $0.50. It is expected that SS Spread may further reduce next week, indicating a trend of balancing in the bunker market. For more information, refer to the “Differentials” section at www.mabux.com.
Global inventories of liquefied natural gas have increased this month driven by weaker demand, while demand is about to recover in the summer. At 550,000 ton as of April 20, LNG in floating storage around the world is almost twice as much as it was this time last year. The increase in inventories is driven chiefly by lower demand from the three biggest LNG importers in the world: China, Japan, and South Korea. China cautioned that the outlook on the country’s LNG demand this year was uncertain, even though gas demand as a whole was seen rising. Japan, meanwhile, is looking for long-term supply and as part of efforts to secure that. In South Korea, a reconsideration of nuclear energy is threatening long-term demand for LNG.
The price of LNG as bunker fuel in the port of Rotterdam continued to decrease, reaching 830 USD/MT on April 25 (minus 6 USD compared to the previous week). The price difference between LNG and conventional fuel also narrowed to 103 USD on April 25, with MGO LS in the port of Rotterdam quoted at 727 USD/MT on that day. We expect that the price difference will further narrow in the upcoming week. For more information, refer to the LNG Bunkering section on mabux.com.
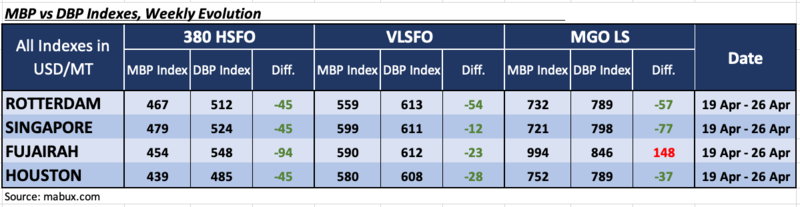
During Week 17, the MDI index, which reflects the correlation between MABUX market bunker prices (MBP Index) and the MABUX digital bunker benchmark (DBP Index), recorded an underpricing of 380 HSFO at all four selected ports. The average weekly undervaluation ratio showed a slight reduction (minus $2 and minus $8) in Rotterdam and Fujairah. In Singapore, the MDI rose by $1, while in Houston, it remained unchanged.
In the VLSFO segment, according to MDI, fuel also remained undervalued in all selected ports. Underprice levels remained virtually unchanged in all ports except for Houston, where the MDI showed a 6-point decline.
In the MGO LS segment, three ports are still underestimated: Rotterdam, Singapore and Houston. The average weekly undervaluation premium decreased in Rotterdam and Singapore by minus 2 and minus 5 points, respectively, but rose by 20 points in Houston. Fujairah remains the only overvalued port.
For more detailed information on the correlation between market prices and the MABUX digital bunker benchmark, you can refer to the "Digital Bunker Prices" section at www.mabux.com. The section is likely to provide additional insights, data, and analysis on bunker fuel prices and their correlation with the digital benchmark.
The European Parliament voted April 18 to include GHG emissions from shipping in the EU Emissions Trading System (ETS), which will mean that at least 20 million ETS allowances – equating to some €2 billion according to the current ETS carbon price – will be channelled into maritime decarbonisation initiatives under the Innovation Fund. The inclusion of shipping in the EU ETS was voted through by 500 votes to 131, with 11 abstentions. The Port of Rotterdam voiced its support of this new legislation, which is part of the EU’s Fit for 55 basket of measures, but at the same time it called for more robust action against any evasion of the ETS. The European Community Shipowners’ Associations (ECSA) also welcomed the passing of the EU ETS legislation, including the allocation of some of its revenue for maritime projects. ECSA also welcomed the upholding of the ‘polluter-pays principle’ through mandatory requirements for the pass-through of the EU ETS costs to the commercial operators of vessels. The organisation noted its support of the inclusion of offshore renewable technologies and carbon capture and storage in the list of strategic net-zero technologies. However renewable fuels of non-biological origin (RFNBOs) should be included in the Act, so that dedicated production capacity can be swiftly developed.
The global bunker market is currently experiencing a moderate downtrend. In the absence of clear drivers, it is anticipated that this trend will persist in the coming week.
By Sergey Ivanov, Director, MABUX