The Weekly Outlook was contributed by Marine Bunker Exchange (MABUX)
Following the results of the 05th week, the MABUX global bunker indices demonstrated moderate growth. The 380 HSFO index rose by 13.81 USD: from 502.49 USD/MT last week to 516.30 USD/MT, firmly exceeding the 500 USD mark. The VLSFO index, in turn, gained 23.51 USD (675.00 USD/MT versus 651.49 USD/MT last week). The MGO index also rose by 24.50 USD (from 894.19 USD/MT last week to 918.69 USD/MT), breaking the 900 USD mark. At the time of writing, the market was undergoing a moderate downward correction.
Global Scrubber Spread (SS) - the price difference between 380 HSFO and VLSFO - continued its directional growth: plus $9.70 ($158.70 versus $149.00 last week). The weekly average also increased by $14.35. In Rotterdam, SS Spread rose by $5.00 (from $124.00 last week to 129.00), firmly exceeding the $100 mark, and the weekly average increasing by $12.16. In Singapore, the price difference for 380 HSFO/VLSFO increased by $6 ($195.00 versus $189.00 last week), breaking through the $200 mark during the week. The weekly average also increased by $26.67. The sustained uptrend of SS Spread enhances the profitability of utilizing the currently cheapest high sulfur fuel HSFO in combination with a scrubber. More information is available in the “Differentials” section of www.mabux.com.
It appears that the oil and gas industry is projected to invest over $1 trillion in natural gas supply, with a significant portion, $223 billion, allocated for developing and operating new gas extraction sites to meet the demand in Europe. Despite a potential structural decline in Europe's gas demand, the continent needs to secure alternative supplies to replace Russian pipeline gas, which was its primary source until 2022. In response to reduced Russian gas deliveries, Europe has shifted its focus to liquefied natural gas (LNG) and increased pipeline supplies from Norway and Africa to fulfill its energy needs. The major players in this substantial investment include ExxonMobil, Shell, TotalEnergies, Equinor, and Eni, collectively expected to spend around $144 billion over the next decade to ensure a stable gas supply for Europe.
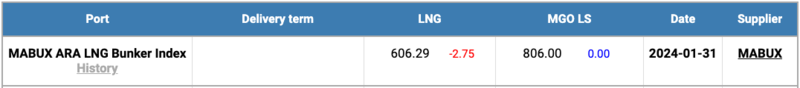
The price of LNG as bunker fuel in the port of Rotterdam (Netherlands) continued its decline, reaching 606 USD/MT on January 31 (minus 2.75 USD compared to last week). Concurrently, the price gap between LNG and conventional fuel widened to 200 USD in favor of LNG versus 169 USD a week earlier. On January 31, MGO LS was quoted at 806 USD/MT in the port of Rotterdam. More information is available in the LNG Bunkering section of www.mabux.com.
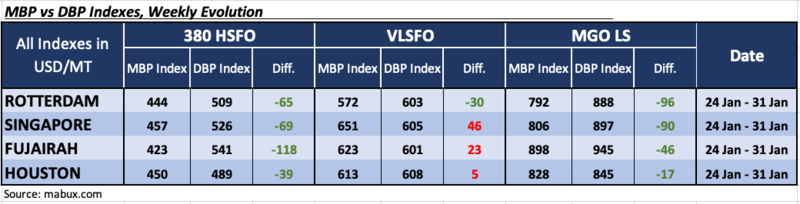
During the 04th week, the MDI index (the ratio of market bunker prices (MABUX MBP Index) vs. the MABUX digital bunker benchmark (MABUX DBP Index)) recorded the following trends in four selected ports: Rotterdam, Singapore, Fujairah and Houston:
In the 380 HSFO segment, all four selected ports were in the underpriced zone. The weekly average underpricing increased by 2 points in Rotterdam, 7 points in Singapore, 1 point in Fujairah and 15 points in Houston. The MDI index in Fujairah consistently exceeds the $100 mark.
In the VLSFO segment, according to MDI, three ports - Singapore, Fujairah, and Houston - were in the overcharge zone. Weekly average overprice premiums rose by 14 points in Singapore, 3 points in Fujairah and 4 points in Houston. The only underpriced port in this bunker fuel segment remains Rotterdam, where the average underprice ratio decreased by 7 points.
In the MGO LS segment, MDI recorded underpricing of this fuel type in all four selected ports. Average weekly premiums increased in Rotterdam by 9 points, in Singapore by 5 points and in Fujairah by 36 points. The MDI index in Houston remained unchanged.
The overall dynamics of the MDI index in the world's largest hubs remains in a phase of irregular changes.
More information on the correlation between market prices and the MABUX digital benchmark is available in the “Digital Bunker Prices” section of www.mabux.com.
A recent study conducted by researchers at Oxford University has determined that a global investment of approximately $2 trillion will be essential to support the infrastructure required for transitioning the worldwide shipping fleet to predominantly utilize green ammonia as a fuel source. It's important to note that these estimated investments exclude expenses related to engine retrofits or the acquisition of new engines. A critical challenge in adopting green ammonia lies in establishing effective connections between the locations where the fuel will be produced and the areas with concentrated shipping demand. The primary investment focus and opportunity for production are anticipated to be in Northern and Western Australia, positioning the region as the main supplier for Asian markets. Additionally, significant production clusters are expected to emerge in Chile (to meet South American demand), California (to address the needs of the western US), North-West Africa (to fulfill European demand), and the southern Arabian Peninsula (to cater to local demand and specific regions in South Asia). While Europe is poised to be a key region for ammonia demand, it is projected to contribute only limited quantities to the overall fuel production.
The Port of Rotterdam reported a decline in the volume of fossil bunker fuels delivered in the fourth quarter of 2023, reaching 1,919,685 metric tonnes – a 15% decrease compared to the previous quarter and a 25% year-on-year decrease. In the same period, sales of bio-blended marine fuels for Q4 2023 totaled 233,108 metric tonnes, showing an increase from the 183,499 metric tonnes in the preceding quarter but a decrease from the 269,739 metric tonnes achieved in the final quarter of 2022. For the entire year of 2023, the total volume of fossil bunker fuels amounted to 9,160,756 metric tonnes, marking a 7% decrease, or 674,986 metric tonnes, compared to the 9,835,742 metric tonnes sold in 2022. The annual total for bio-blended marine fuels in 2023 also declined year-on-year, dropping from 790,851 metric tonnes to 751,638 metric tonnes. LNG sales in the fourth quarter of 2023 amounted to 148,933 cubic meters, reflecting a decrease from the 204,418 cubic meters recorded in the previous quarter but a substantial increase from the 58,599 cubic meters sold in Q4 2022. The total LNG sales for the entire year of 2023 reached 619,243 cubic meters, surpassing the 406,599 cubic meters sold in 2022 by over 50%.
We expect the upward trend to continue dominating the dynamics of global bunker indices in the upcoming week.
By Sergey Ivanov, Director, MABUX
All news