The Bunker Outlook was contributed by Marine Bunker Exchange (MABUX)
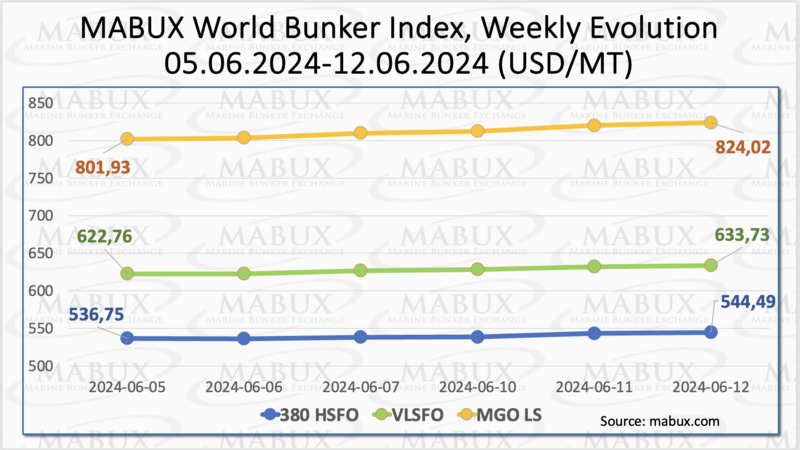
During Week 24, the MABUX global bunker indices showed robust growth across all segments. The 380 HSFO index rose by 7.74 USD, moving from 536.75 USD/MT last week to 544.49 USD/MT. The VLSFO index increased by 10.97 USD (633.73 USD/MT versus 622.76 USD/MT last week). The MGO index saw the most significant rise, adding 22.09 USD (from 801.93 USD/MT last week to 824.02 USD/MT). At the time of writing, the upward trend moderately continued in the global bunker market.
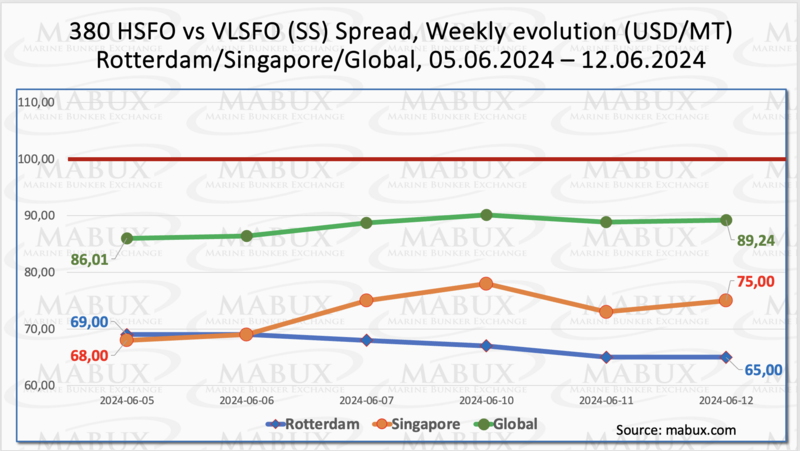
MABUX Global Scrubber Spread (SS) - the price difference between 380 HSFO and VLSFO - experienced a moderate increase: plus $3.23 ($89.24 vs. $86.01 last week). Despite this increase, the spread remains consistently below the critical $100.00 breakeven point. Conversely, the weekly average of the SS decreased by $5.40. In Rotterdam, SS Spread continued its decline, dropping by $4.00 (from $69.00 last week to 65.00). The port's SS weekly average also decreased by $6.50. In Singapore, the price difference for 380 HSFO/VLSFO increased slightly by $7.00 ($75.00 vs. $68.00 last week), with the weekly average adding $7.67. Overall, while the contraction of the SS Spread has paused, the indicators suggest an upward correction may continue into the next week. More information is available in the "Differentials" section of mabux.com.
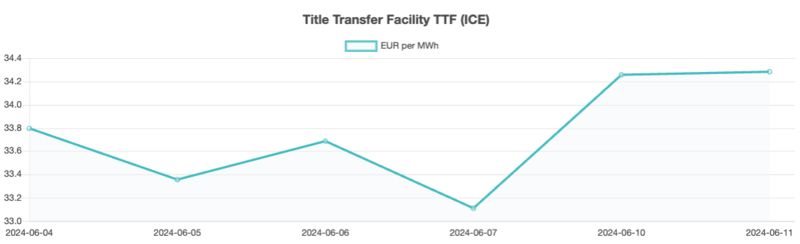
StanChart has reported that there has been no change in the dominant dynamics of the European gas market, with inventories building slower than usual and the markets remaining highly sensitive to supply issues. EU gas inventories stood at 81.75 billion cubic meters (bcm) on 2 June, showing a year-on-year increase of 1.1 bcm and a surplus of 14.9 bcm above the five-year average. However, experts note that the surplus above the five-year average has decreased on 45 of the past 48 days. StanChart predicts that prices are likely to remain elevated, bolstered by slower-than-average inventory builds. In Week 24, the European gas benchmark TTF rose moderately by 0.488 EUR/MWh, from 33.797 EUR/MWh to 34.285 EUR/MWh.
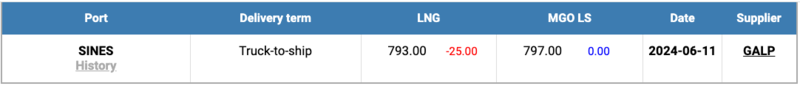
Meanwhile, the price of LNG as bunker fuel in the port of Sines (Portugal) decreased slightly, reaching 793 USD/MT on June 11 (minus 25 USD compared to last week). Meanwhile, the price gap between LNG and conventional fuel almost closed. On June 11, LNG was priced just 4 USD below MGO LS, a significant change from a week earlier when MGO LS was 14 USD cheaper. On June 11, MGO LS was quoted at 797 USD/MT in the port of Sines. More information is available in the LNG Bunkering section of mabux.com.
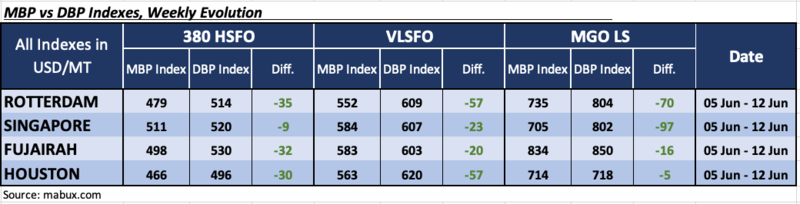
In Week 24, the MDI index (the correlation ratio of market bunker prices (MABUX MBP Index) vs. MABUX digital bunker benchmark (MABUX DBP Index)) revealed the following trends across the major global hubs: Rotterdam, Singapore, Fujairah and Houston:
In the 380 HSFO segment, Singapore returned to an undervalued position, making all selected ports underpriced. The weekly averages widened by 5 points in Rotterdam, 11 points in Singapore, 1 point in Fujairah, and 4 points in Houston.
In the VLSFO segment, according to the MDI, all ports were undervalued, with average weekly underprice levels increasing by 10 points in Rotterdam, 2 points in Singapore, 3 points in Fujairah, and 18 points in Houston.
In the MGO LS segment, Houston returned to the undervalued zone, joining the other ports in this bunker fuel segment. Average weekly levels increased by 7 points in Rotterdam, 1 point in Fujairah, and 14 points in Houston, but decreased by 2 points in Singapore, dropping the MDI index in Singapore below $100.
At the end of the week, the balance of overvalued/undervalued ports underwent significant changes: all segments of bunker fuel were undervalued in all selected ports. We expect this trend of underpricing of fuel to continue into the next week.
For more details on the correlation between market prices and the MABUX digital benchmark, visit the “Digital Bunker Prices” section on mabux.com.
According to the report from DNV, 33 new orders for alternative-fuelled vessels were placed in May, with 23 of these orders being for methanol-fuelled vessels. Among the methanol-fuelled vessel orders, 10 were for the container segment, five were for bulk carriers, and four were for car carriers. The remaining alternative-fuelled vessel orders for May included eight for LNG and two for ammonia. So far in 2024, there have been a total of 127 new orders for alternative-fuelled vessels, marking a 55% increase compared to the first five months of 2023. Methanol has emerged as the leading alternative fuel segment this year, with 70 new orders for methanol-fuelled vessels, accounting for 55% of all new orders for alternative-fuelled vessels in 2024. Although methanol is still behind LNG in overall terms, these recent figures indicate a significant and growing interest in methanol-fuelled vessels from the market. Last month’s orders for ammonia-fuelled vessels brought the total for 2024 to 11 – nine more than were ordered during the whole of 2023.
We anticipate a sustained upward trend in the global bunker market into the next week.
By Sergey Ivanov, Director, MABUX
All news