The Bunker Outlook was contributed by Marine Bunker Exchange (MABUX)
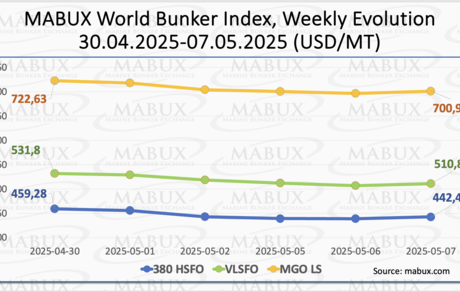
At the end of Week 19, the MABUX Global bunker indices showed a downward trend. The 380 HSFO index dropped by 16.81 USD, falling from 459.28 USD/MT to 442.47 USD/MT and breaking below the 450.00 USD threshold. The VLSFO index declined by 20.92 USD, from 531.80 USD/MT to 510.88 USD/MT, nearing the 500.00 USD mark. Meanwhile, the MGO index decreased by 21.64 USD, from 722.63 USD/MT to 700.99 USD/MT. At the time of writing, the market was showing signs of a moderate upward correction.
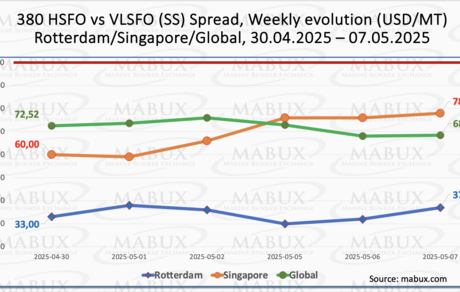
The MABUX Global Scrubber Spread (SS) – the price difference between 380 HSFO and VLSFO – continued its moderate decline, dropping by $4.11 from $72.52 to $68.41, falling below the $70.00 threshold. The weekly average of the global index also slipped by $0.37. In Rotterdam, the SS Spread moved in the opposite direction, rising by $4.00 to $37.00 from $33.00 the previous week, though still remaining under the $40.00 mark. The weekly average in the port saw a marginal increase of $0.16. Singapore posted a more pronounced increase in the 380 HSFO/VLSFO differential, up by $18.00 from $60.00 to $78.00, with the weekly average gaining $9.67. Currently, no significant shifts have been observed in the overall dynamics of the global and port SS Spread indices. All values remain well below the $100.00 SS breakeven point, indicating that VLSFO continues to offer greater profitability compared to the 380 HSFO + scrubber option. We expect SS Spread levels to remain stable in the coming week. Further details can be found in the "Differentials" section of mabux.com.
According to a new report from the Institute for Energy Economics and Financial Analysis (IEEFA), the European Union reduced its combined imports of pipeline gas and liquefied natural gas (LNG) by 18% between 2021 and 2024, in line with a 20% drop in overall gas consumption. In 2024, Norway emerged as the EU's largest supplier of pipeline gas, while the United States was the leading supplier of LNG. During the first quarter of 2025, Norway accounted for 30% of the EU’s total gas and LNG supply, followed by the United States with 25%, Russia with 14%, and Algeria with 13%.
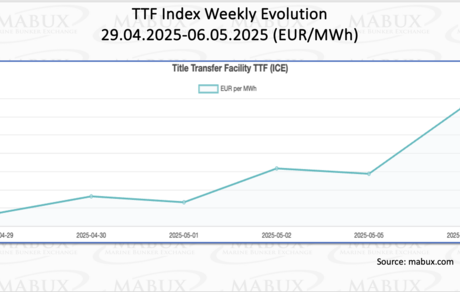
As of May 6, European regional gas storage facilities were filled to 41.41%, reflecting an increase of 1.89% compared to the previous week. However, this represents a significant decrease of 29.92% compared to the beginning of the year, when storage levels stood at 71.33%. Despite the seasonal decline, gas reserves in EU storage facilities have resumed a gradual upward trend. At the end of Week 19, the European gas benchmark TTF recorded an increase of 2.89 euros/MWh, rising from 31.856 euros/MWh the previous week to 34.743 euros/MWh.
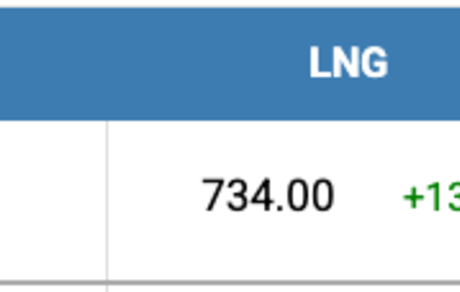
The price of LNG as a bunker fuel in the port of Sines (Portugal) increased by 13 USD by the end of the week and reached 734 USD/MT against 721 USD/MT the week before. At the same time, the difference in the price between LNG and conventional fuel on May 5 was 77 USD in favor of conventional fuel against 42 USD the week before: MGO LS was quoted on this day in the port of Sines at 657 USD/MT. More detailed information is available in the LNG Bunkering section on the www.mabux.com website.
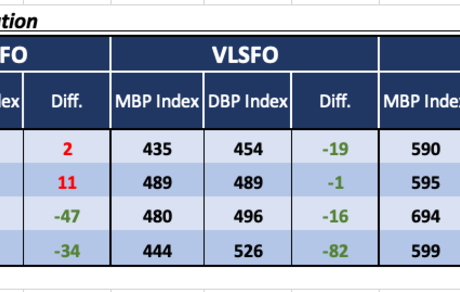
Over Week 19, the MABUX Market Differential Index (MDI) – which reflects the ratio between market bunker prices (MBP) and the MABUX Digital Bunker Benchmark (DBP) – showed the following trends across the 380 HSFO, VLSFO, and MGO LS segments:
• 380 HSFO segment: Rotterdam entered the overvalued zone, joining Singapore. The average weekly MDI values increased by 3 points in Rotterdam and 4 points in Singapore. The remaining two ports were undercharged: Fujairah's underpricing deepened by 4 points, while Houston saw a 7-point reduction in its undervaluation. Notably, Rotterdam remained at the 100% correlation level between MBP and DBP.
• VLSFO segment: All four monitored ports remained in the undervalued zone. The average weekly MDI values declined by 16 points in Rotterdam, 19 points in Singapore, 15 points in Fujairah, and 23 points in Houston. Singapore is currently approaching a 100% correlation between MBP and DBP.
• MGO LS segment: Rotterdam continued to be the only overvalued port, although its weekly average MDI fell by 5 points. The other ports remained undervalued, with the MDI decreasing by 11 points in Singapore, 15 points in Fujairah, and 23 points in Houston. Rotterdam remains close to full MBP-DBP correlation.
Overall, no major shifts were observed in the overvaluation/undervaluation structure during the week, apart from Rotterdam’s transition into the overvalued zone in the 380 HSFO segment. Based on current market conditions, we do not anticipate significant changes in the MDI balance next week.
For more details on the correlation between market prices and the MABUX digital benchmark, visit the Digital Bunker Prices section at mabux.com.
The Bureau Veritas VeriFuel Bunker Fuel Quality Report for Q1 2025 indicates a global increase in the average viscosity of very low sulphur fuel oil (VLSFO). The average viscosity rose from 161 cSt (at 50°C) in Q4 2024 to 173 cSt in Q1 2025. This marks a consistent month-on-month rise, with average viscosities of 168 cSt in January, 174 cSt in February, and 177 cSt in March.
Other notable changes in global average parameters for VLSFO include:
Sediment content: Increased slightly from 14.3% in Q4 2024 to 14.5% in Q1 2025.
Catalytic fines: Rose from 27.5% to 30.6%.
Off-spec VLSFO: Increased from 1.5% to 1.8%.
For high-sulphur fuel oil (HSFO), the average viscosity (at 50°C) decreased slightly from 310 cSt in Q4 2024 to 307 cSt in Q1 2025. However, the global average off-spec HSFO rose by 1.1 percentage points, reaching 1.8%. Meanwhile, the global average off-spec DMA (0.10%) improved, declining from 2.7% in Q4 2024 to 2.2% in Q1 2025.
The global bunker market has shown signs of a moderate upward correction following a week of consistent price declines. Looking ahead, we expect that bunker indices may retain the potential to continue an upward trend into next week.
By Sergey Ivanov, Director, MABUX